5 Key Factors Driving Automotive Industry Growth
Understand the five crucial factors propelling growth in the global automotive industry.
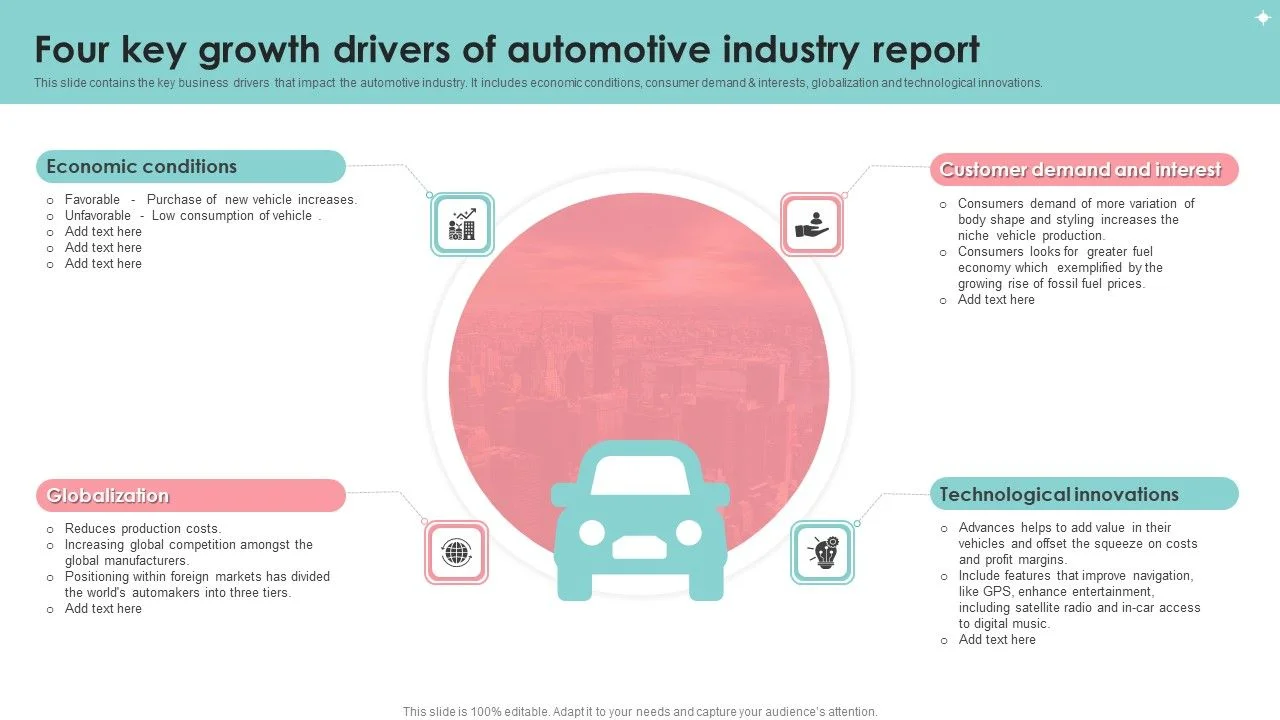
5 Key Factors Driving Automotive Industry Growth
Hey there, car enthusiasts and industry watchers! Ever wonder what’s really pushing the automotive world forward? It’s not just about shiny new models hitting the showrooms. There are some massive forces at play, shaping how cars are made, sold, and even how we think about getting around. Today, we’re diving deep into the 5 Key Factors Driving Automotive Industry Growth, with a special look at how these trends are playing out in the US and Southeast Asian markets. We’ll cover everything from electric vehicles to smart tech, and even how consumer habits are changing the game. So, buckle up!
Electrification and Sustainable Mobility The EV Revolution
First up, and probably the most talked-about factor, is the massive shift towards electrification. We’re not just talking about a few electric cars here and there; this is a full-blown revolution. Governments worldwide, especially in places like the US and various Southeast Asian nations, are pushing hard for greener transportation. This means big incentives for buyers, stricter emissions regulations for manufacturers, and huge investments in charging infrastructure.
Government Policies and Incentives Driving EV Adoption
In the United States, federal tax credits for new EV purchases can be up to $7,500, making electric cars much more appealing. States like California also offer their own rebates, sometimes adding another few thousand dollars to the savings. This kind of financial push is a huge motivator for consumers to make the switch. For example, a Tesla Model 3, which might seem pricey at first glance, becomes a lot more competitive when you factor in these incentives.
Over in Southeast Asia, countries like Thailand, Indonesia, and Vietnam are also rolling out the red carpet for EVs. Thailand, for instance, has set ambitious targets for EV production and adoption, offering tax breaks and subsidies that make brands like BYD and NETA incredibly popular. Indonesia is focusing on becoming a global hub for EV battery production, leveraging its vast nickel reserves, which in turn supports local EV manufacturing. Vietnam’s VinFast is a prime example of a local player making significant strides, even expanding into the US market.
Technological Advancements in EV Batteries and Range
Beyond incentives, the tech itself is getting seriously good. Battery technology is improving at a rapid pace. We’re seeing longer ranges, faster charging times, and more affordable battery production. A few years ago, an EV with a 200-mile range was considered excellent; now, many models easily exceed 300 miles on a single charge. This reduces range anxiety, which has been a major barrier for many potential EV buyers.
Consider the Lucid Air Grand Touring, which boasts an EPA-estimated range of over 500 miles – that’s incredible! While it’s a premium vehicle, the technology trickles down to more affordable options. Even mainstream models like the Hyundai Ioniq 5 and Kia EV6 offer impressive ranges of over 300 miles, making them practical for most drivers. These advancements are crucial for widespread adoption, especially in regions where charging infrastructure might still be developing.
Expansion of Charging Infrastructure and Ecosystems
Of course, an EV is only as good as its charging network. Both the US and Southeast Asia are seeing massive investments here. In the US, companies like Electrify America and EVgo are rapidly expanding their fast-charging networks. Tesla’s Supercharger network, once exclusive, is now opening up to other EV brands, which is a game-changer for interoperability.
In Southeast Asia, governments and private companies are collaborating to build out charging stations. Singapore, for example, has a dense network of public chargers. Thailand is also seeing a surge in charging points, often integrated into shopping malls and rest stops. The goal is to make charging an EV as convenient as filling up a gas tank, and while we’re not quite there yet, progress is undeniable.
Technological Innovation and Digitalization Smart Cars and Connectivity
The second major driver is the relentless march of technology. Cars are no longer just mechanical beasts; they’re becoming sophisticated computers on wheels. This includes everything from advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to seamless in-car connectivity.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems ADAS and Safety Features
ADAS features are making cars safer and easier to drive. Think adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, automatic emergency braking, and blind-spot monitoring. These systems are becoming standard even in entry-level vehicles. Brands like Subaru with its EyeSight system, and Toyota with Safety Sense, have made these technologies accessible to a wider audience. The goal is to reduce accidents and improve overall road safety, which is a win for everyone.
For example, Volvo’s commitment to safety has led to innovations like pedestrian and cyclist detection systems. These features are not just about convenience; they’re about preventing serious injuries and fatalities. As these technologies become more refined and reliable, they’ll continue to drive consumer demand for newer, safer vehicles.
In-Car Connectivity Infotainment and Telematics
Modern cars are also becoming extensions of our digital lives. Infotainment systems with large touchscreens, smartphone integration (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto), and built-in navigation are now expected. Telematics systems, which collect data on vehicle usage and performance, are also becoming more common, offering services like remote diagnostics, stolen vehicle recovery, and even personalized insurance rates.
The Mercedes-Benz MBUX system, for instance, uses artificial intelligence to learn driver preferences and respond to natural language commands. Similarly, BMW’s iDrive system has evolved to offer intuitive control over a vast array of functions. In Southeast Asia, local brands and joint ventures are also integrating advanced infotainment, often tailored to regional apps and services. This connectivity enhances the driving experience, making commutes more enjoyable and productive.
Over-the-Air OTA Updates and Software Defined Vehicles
One of the most exciting developments is the rise of software-defined vehicles. This means cars can receive over-the-air (OTA) updates, just like your smartphone. This allows manufacturers to add new features, improve performance, and even fix bugs without requiring a trip to the dealership. Tesla pioneered this, and now many other brands, including Ford with its Power-Up updates and GM with Ultifi, are following suit.
This capability means your car can actually get better over time, rather than becoming outdated. It also opens up new revenue streams for manufacturers through subscription services for certain features, like enhanced ADAS capabilities or performance upgrades. This shift from hardware-centric to software-centric development is fundamentally changing the automotive business model.
Changing Consumer Preferences and Demographics The SUV Craze and Urban Mobility
The third factor is all about us – the consumers! Our tastes, needs, and even our living situations are constantly evolving, and the automotive industry has to keep up.
The Dominance of SUVs and Crossovers
Globally, and especially in the US and Southeast Asia, SUVs and crossovers are king. People love the higher driving position, the perceived safety, the extra cargo space, and the versatile styling. Sedans are still around, but their market share has shrunk considerably. This trend has led manufacturers to pour resources into developing a wide range of SUV models, from compact crossovers to full-size family haulers.
In the US, best-sellers like the Toyota RAV4, Honda CR-V, and Ford Explorer consistently top sales charts. In Southeast Asia, models like the Mitsubishi Xpander and Honda HR-V are incredibly popular, often serving as family vehicles that can handle diverse road conditions. This shift means automakers must continually innovate in the SUV segment to capture market share.
Demand for Personalized and Connected Experiences
Today’s buyers want more than just a way to get from A to B. They want a personalized experience. This includes customizable interiors, advanced infotainment systems, and seamless integration with their digital lives. The ability to choose specific features, colors, and trim levels is more important than ever.
Furthermore, the younger generation, particularly millennials and Gen Z, are looking for vehicles that align with their values, such as sustainability and technological sophistication. They are also more open to alternative ownership models, which brings us to the next point.
Rise of Mobility as a Service MaaS and Car Sharing
In urban centers, especially in densely populated Southeast Asian cities like Bangkok, Jakarta, and Manila, traditional car ownership is becoming less appealing for some. Traffic congestion, parking difficulties, and high costs are pushing people towards Mobility as a Service (MaaS) solutions. This includes ride-hailing (Grab, Gojek), car-sharing (Zipcar, SOCAR), and even subscription-based car services.
Companies like Grab and Gojek have transformed urban transportation in Southeast Asia, offering not just rides but also food delivery and logistics. In the US, services like Zipcar provide convenient access to vehicles without the burdens of ownership. This trend means automakers are not just selling cars; they’re also exploring partnerships and investments in these mobility services to stay relevant in a changing landscape.
Global Economic Shifts and Market Dynamics Emerging Markets and Supply Chains
The fourth factor is the broader economic picture. Global trade, economic growth, and even geopolitical events all play a significant role in the automotive industry’s health.
Growth in Emerging Markets Particularly Southeast Asia
While mature markets like the US remain crucial, much of the automotive industry’s growth is now coming from emerging economies. Southeast Asia, with its growing middle class and increasing urbanization, is a prime example. Countries like Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines are seeing rising disposable incomes, leading to increased demand for personal vehicles.
Manufacturers are heavily investing in these regions, setting up production facilities and tailoring models to local tastes and road conditions. For instance, many Japanese and Korean brands have a strong presence in Southeast Asia, offering reliable and affordable vehicles that resonate with local buyers. The potential for growth in these markets is enormous, making them a key focus for global automakers.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions and Geopolitical Tensions
The past few years have highlighted the fragility of global supply chains. The semiconductor shortage, in particular, brought vehicle production to a crawl, costing the industry billions. Geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and even natural disasters can all disrupt the flow of parts and materials, impacting production and vehicle availability.
This has led automakers to rethink their supply chain strategies, focusing on diversification, regionalization, and building greater resilience. Companies are looking to source components closer to their manufacturing plants and reduce reliance on single suppliers. This shift is not just about efficiency; it’s about ensuring continuity of production in an increasingly unpredictable world.
Inflationary Pressures and Raw Material Costs
Rising inflation and the increasing cost of raw materials (like lithium, nickel, and steel) are also significant factors. These costs directly impact vehicle prices, potentially making new cars less affordable for consumers. Automakers are constantly looking for ways to absorb some of these costs through efficiency gains or pass them on to consumers, which can affect sales volumes.
The balance between offering competitive pricing and maintaining profitability is a constant challenge, especially in a market where consumers are becoming more price-sensitive. This pressure also accelerates the search for alternative materials and more efficient manufacturing processes.
Sustainability and Environmental Regulations The Green Imperative
Finally, the push for sustainability and stricter environmental regulations is a powerful force shaping the industry. This goes beyond just EVs and touches on every aspect of vehicle production and lifecycle.
Stricter Emissions Standards and Fuel Economy Regulations
Governments around the world are implementing increasingly stringent emissions standards. In the US, the EPA and NHTSA set fuel economy and emissions targets that push manufacturers to produce cleaner vehicles. Similar regulations are in place across Europe and are emerging in many Southeast Asian countries.
These regulations are a primary driver for the development of electric, hybrid, and more fuel-efficient internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Failure to meet these standards can result in hefty fines, providing a strong incentive for automakers to innovate in green technologies.
Circular Economy Principles and Sustainable Manufacturing
Beyond just tailpipe emissions, there’s a growing focus on the entire lifecycle of a vehicle. This includes sustainable manufacturing processes, reducing waste, using recycled materials, and improving the recyclability of vehicles at the end of their life. The concept of a ‘circular economy’ is gaining traction, where resources are kept in use for as long as possible.
Companies like BMW are exploring ways to use more recycled plastics and sustainable materials in their interiors. The recycling of EV batteries is also a huge area of focus, with companies investing in technologies to recover valuable materials like lithium and cobalt. This commitment to sustainability is not just about compliance; it’s also about brand image and meeting consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Corporate Social Responsibility CSR and Brand Image
Consumers, particularly in developed markets like the US, are increasingly conscious of a company’s environmental and social impact. Automakers are responding by emphasizing their Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives, from reducing their carbon footprint in manufacturing to supporting local communities.
A strong CSR strategy can enhance brand loyalty and attract environmentally conscious buyers. This means transparent reporting on sustainability efforts, ethical sourcing of materials, and fair labor practices are becoming just as important as vehicle performance and design. Brands that genuinely embrace sustainability are likely to thrive in the long run.
So there you have it – the five big factors that are really driving the automotive industry forward. From the electric revolution to smart tech, changing consumer tastes, global economics, and the undeniable push for sustainability, it’s a dynamic and exciting time to be involved with cars. Keep an eye on these trends, because they’re not just shaping the vehicles of today, but also the way we’ll all be moving around tomorrow!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)